Throughout the course of comprehensive healthcare, many patients develop problems with their minds and bodies that can lead to severe discomfort, costly treatment, disabilities, and more. Predicting those escalations in advance offers healthcare providers the opportunity to apply preventative measure that might improve patient safety, and quality of care, while lowering medical costs. In simple terms, prediction using networks of big data used to evaluate specific people, and specific risk factors in certain illnesses could save lives, and avoid medical complications.
Today, many prognostics methods turn to Artificial Neural Networks when attempting to find new insights into the future of patient healthcare. ANNs (Artificial Neural Networks) are just one of the many models being introduced into the field of healthcare by innovations like AI and big data. Their purpose is to transform huge amounts of raw data into useful decisions for treatment and care.
What is a Neural Network?
Understanding Neural Networks can be very difficult. After all, to many people, these examples of Artificial Intelligence in the medical industry are a futuristic concept.
According to Wikipedia (the source of all truth) :
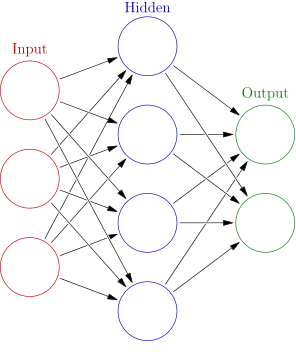
“Neural Networks are a computational approach which is based on a large collection of neural units loosely modeling the way the brain solves problems with large clusters of biological neurons connected by axons. Each neural unit is connected with many others…These systems are self-learning and trained rather than explicitly programmed…”
By Glosser.ca – Own work, Derivative of File:Artificial neural network.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
One way to think of it is this: Imagine that a doctor wants to make a prediction regarding a patient’s health – for instance, whether she or he is at risk of suffering from a certain disease. How would a doctor be able to ascertain that information? In most cases, it would involve using blood tests, taking tests of the patient’s vitals, and more to identify features that have proven to be good predictors of patient health. However, what if doctors only know a handful of risk-factors for a specific disease – or worse, they don’t know the risk factors at all? It would be impossible to make predictions.
ANNs help to provide the predictions in healthcare that doctors and surgeons simply couldn’t address alone. They work in moments wherein we can collect data, but we don’t understand which pieces of that data are vitally important yet. These abstractions can therefore capture complex relationships that might not be initially obvious – leading to better prediction for public health.
What are the Possibilities for Neural Networks in Healthcare?
Though they may seem like a futuristic concept, ANNs have been used in healthcare for several decades. In fact, the book “Neural Networks in Healthcare” covers the various uses of this system prior to 2006. Before 2006, the main successes of ANNs were found in areas like speech processing and image processing. Today, as new technologies emerge, capable of changing the way that we approach neural networks in the first place – it’s worth noting that there may be numerous new options for changing the industry. Today, the possibilities for Neural Networks in Healthcare include:
- Diagnostic systems – ANNs can be used to detect heart and cancer problems, as well as various other diseases informed by big data.
- Biochemical analysis – ANNs are used to analyze urine and blood samples, as well as tracking glucose levels in diabetics, determining ion levels in fluids, and detecting various pathological conditions.
- Image analysis – ANNs are frequently used to analyze medical images from various areas of healthcare, including tumor detection, x-ray classifications, and MRIs.
- Drug development – Finally, ANNs are used in the development of drugs for various conditions – working by using large amounts of data to come to conclusions about treatment options.
Current Examples of Neural Networks
Neural networks can be seen in most places where AI has made steps within the healthcare industry. For instance, in the world of drug discovery, Data Collective and Khosla Ventures are currently backing the company “Atomwise“, which uses the power of machine learning and neural networks to help medical professionals discover safer and more effective medicines fast. The company recently published its first findings of Ebola treatment drugs last year, and the tools that Atomwise uses can tell the difference between toxic drug candidates and safer options.
Similarly, options are being found that could insert neural networks into the realm of diagnostic. For instance, in 2014, Butterfly Networks, which are transforming the diagnostic realm with deep learning, devices, and the cloud, raised $100M for their cause. This organization currently works at the heart of the medicine and engineering sectors by bringing together world-class skills in everything from electrical engineering, to mechanical engineering, and medicine. At the same time, iCarbonX are developing artificial intelligence platforms to facilitate research relating to the treatment of various diseases and preventative care. The company believe that soon they will be able to help enable the future of truly personalized medicine.
The Future of Healthcare…
Perhaps the most significant problem with ANNs is that the learned features involved when it comes to assessing huge amounts of data can sometimes be difficult to interpret. This is potentially why ANNs are more commonly used during situations wherein we have a lot of data to ensure that the observed data doesn’t contain too many “flukes”. Think of it this way – if you toss a coin three times and receive “tails” every time, this doesn’t mean that a coin only has a “tails” side. It just means that you need further evaluation and more testing to get a proper reading of probability.
ANNs are going to need some tweaking if they’re going to become the change that the healthcare industry needs. However, alongside new AI developments, it seems that neural networks could have a very important part to play in the future of healthcare.